

On the other hand, if you use a new Double(String value) constructor then you will always get a new Double object, creating memory pressure for your application.īTW, in this article, we will not only learn how to convert String to double value but also how to convert Double to String, as it's important to know both sides of a conversion.

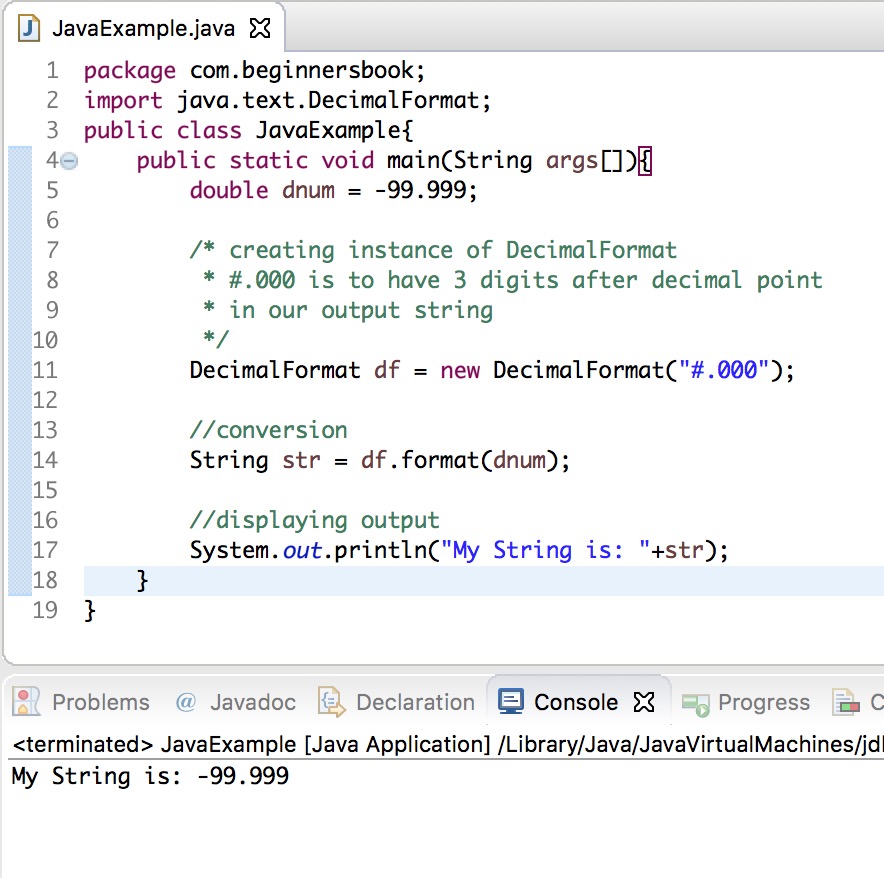
Some of you might be curious and thinking if one method can do the job then why we have three methods for String to Double or double conversion? Well, their purpose is a little bit different and they also provide some other service.įor example, you should be using Double.valueOf() method if you frequently need to convert String to Double because it will likely give better performance by caching frequently used values just like Integer.valueOf() method does. This method will throw NullPointerException if the string you are passing is null and NumberFormatExceptionif String is not containing a valid double value e.g. Rest of the methods like valueOf() and constructor uses parseDouble() internally. Out of all these methods, the core method is parseDouble() which is specially designed to parse a String containing floating-point value into the Double object. There are three ways to convert a String to double value in Java, Double.parseDouble() method, Double.valueOf() method and by using new Double() constructor and then storing the resulting object into a primitive double field, autoboxing in Java will convert a Double object to the double primitive in no time.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
